The Toyota Production System (TPS) is an integrated socio-technical system, developed by Toyota, that comprises its management philosophy and practices. The TPS organizes manufacturing and logistics for the automobile manufacturer, including interaction with suppliers and customers. The system is a major precursor of the more generic “lean manufacturing“. Taiichi Ohno and Eiji Toyoda, Japanese industrial engineers, developed the system between 1948 and 1975.
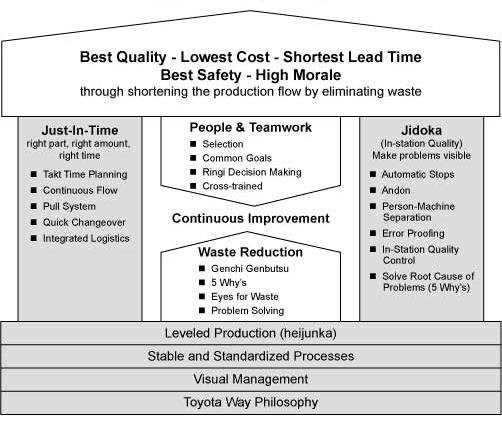
Goals
The main objectives of the TPS are to design out overburden (muri) and inconsistency (mura), and to eliminate waste (muda). The most significant effects on process value delivery are achieved by designing a process capable of delivering the required results smoothly; by designing out “mura” (inconsistency). It is also crucial to ensure that the process is as flexible as necessary without stress or “muri” (overburden) since this generates “muda” (waste). Finally the tactical improvements of waste reduction or the elimination of muda are very valuable. There are eight kinds of muda that are addressed in the TPS:[2]
- Waste of overproduction (largest waste)
- Waste of time on hand (waiting)
- Waste of transportation
- Waste of processing itself
- Waste of stock at hand
- Waste of movement
- Waste of making defective products
- Waste of underutilized workers
The elimination of waste has come to dominate the thinking of many when they look at the effects of the TPS because it is the most familiar of the three to implement. In the TPS many initiatives are triggered by inconsistency or over-run reduction which drives out waste without specific focus on its reduction.
Principles
The underlying principles, called the Toyota Way, have been outlined by Toyota as follows:
Continuous improvement:
- Challenge (We form a long-term vision, meeting challenges with courage and creativity to realize our dreams.)
- Kaizen (We improve our business operations continuously, always driving for innovation and evolution.)
- Genchi Genbutsu (Go to the source to find the facts to make correct decisions.)
Respect for people:
- Respect (We respect others, make every effort to understand each other, take responsibility and do our best to build mutual trust.)
- Teamwork (We stimulate personal and professional growth, share the opportunities of development and maximize individual and team performance.)
External observers have summarized the principles of the Toyota Way as:
Long-term philosophy:
1.Base your management decisions on a long-term philosophy, even at the expense of short-term financial goals.
The right process will produce the right results:
1. Create continuous process flow to bring problems to the surface.
2. Use the “pull system” to avoid overproduction.
3. Level out the workload (heijunka). (Work like the tortoise, not the hare.)
4. Build a culture of stopping to fix problems, to get quality right from the start.
5. Standardized tasks are the foundation for continuous improvement and employee empowerment.
6. Use visual control so no problems are hidden.
7. Use only reliable, thoroughly tested technology that serves your people and processes.
Add value to the organization by developing your people and partners:
1. Grow leaders who thoroughly understand the work, live the philosophy, and teach it to others.
2. Develop exceptional people and teams who follow your company’s philosophy.
3. Respect your extended network of partners and suppliers by challenging them and helping them improve.
Continuously solving root problems drives organizational learning:
1. Go and see for yourself to thoroughly understand the situation (Genchi Genbutsu, 現地現物);
2. Make decisions slowly by consensus, thoroughly considering all options (Nemawashi, 根回し); implement decisions rapidly;
3. Become a learning organization through relentless reflection (Hansei, 反省) and continuous improvement and never stop (Kaizen, 改善).
Reference:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Toyota_Production_System


There are 0 comments